Statefulset
Statefulset application is Statefulsetset. For more details about Statefulsetset, please see kubernets official documentation-Statefulset.
Pod is the smallest orchestration unit of Kubernetes, and statefulset statefulset is mainly used to deploy statefulset applications with non-reciprocal relationships between instances and instances with dependencies on external data. Applications deployed based on statefulset have the following characteristics.
- Pods deployed based on statefulset are sequential, and the order is maintained after migration or destruction and reconstruction of pods.
- if persistent storage is required, PVC-based persistent storage can be implemented.
- headless service-based implementation of stable network flags.
Entry: In the cloud management platform click the top left corner navigation menu, click “Container/Applications/Statefulset” menu item in the left menu bar that pops up to enter the Statefulset page.
navigation menu, click “Container/Applications/Statefulset” menu item in the left menu bar that pops up to enter the Statefulset page.
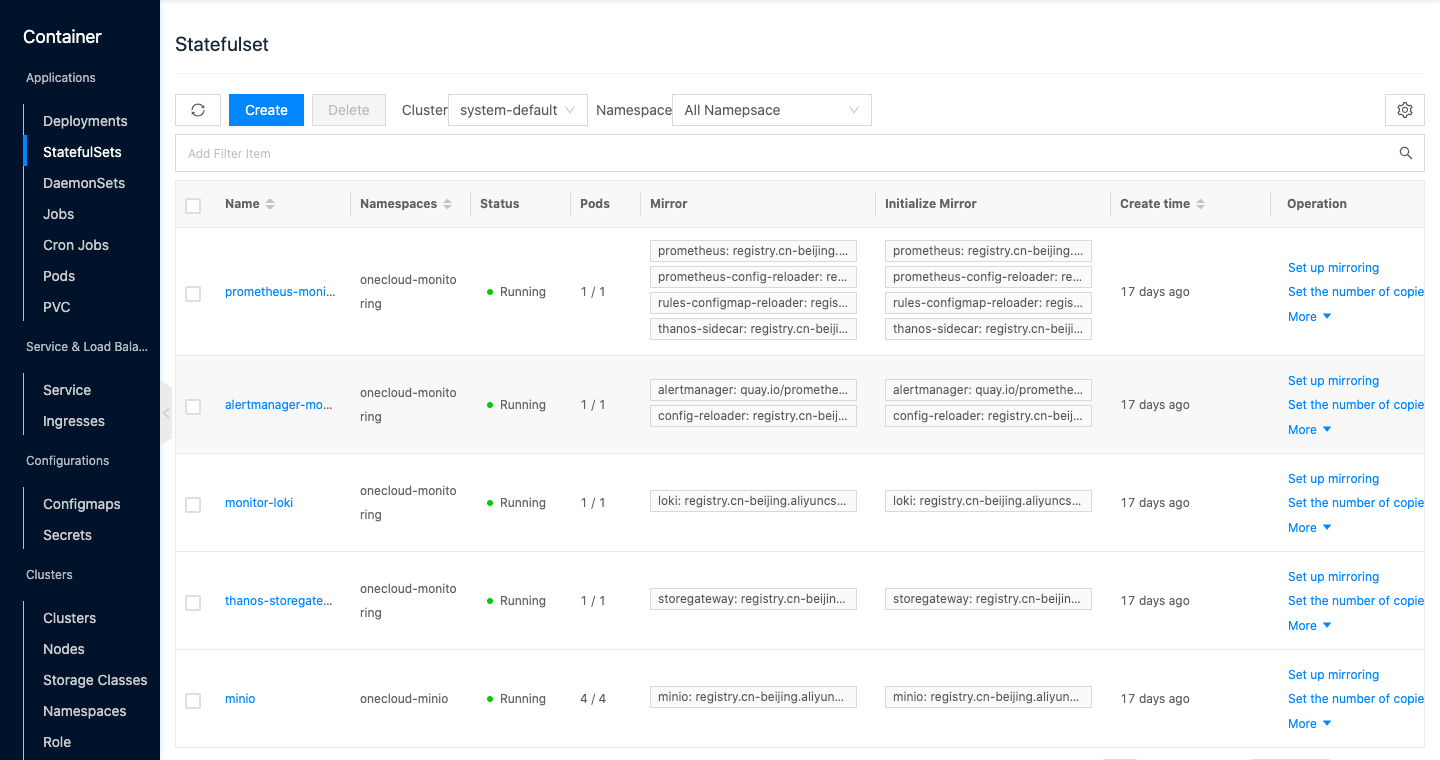
View Statefulset Applications
This function is used to filter statefulset application information based on clusters and namespaces.
-
In the statefulset page, by default, you can view the statefulset application information of all namespaces under a cluster.
-
When there are multiple clusters in the environment, click the cluster input box on the right side of the list and select other clusters to view the statefulset application information of all namespaces under other clusters.
-
When there are multiple namespaces under the cluster, click the input box on the right side of the namespace above the list, select the namespace, and view the statefulset application information under the specified namespace.
Create Statefulset Application
This function is used to create a statefulset application Statefulsetset by mirroring.
-
On the Statefulsetset page, click the “Create” button at the top of the list to enter the Create Statefulsetset page.
-
Set the following parameters.
- Name: The name of the Statefulsetset.
- Cluster: Select the cluster to which the statefulset application belongs.
- Namespace: Select the namespace to which the statefulset application belongs. The namespace is used to logically divide the cluster. deployment, pod, service, etc. all belong to a namespace. Kubernetes cluster will generate default, kube-system, kube-public and other namespaces by default after the cluster is created.
- Number of container groups: Set the number of container group Pods, which corresponds to the spec.replicas value in the yaml file.
- Image key: you need to set the key when accessing private repository, support new and select existing key.
- Service: Set the access method for statefulset applications and container groups, including internal access and external access to the cluster.
- Internal: A ClusterIP will be automatically generated for access inside the cluster and between container groups.
- Target port: The target port is the port on the pod.
- Service port: The user access port.
- Protocol: Select the protocol used by the application, including TCP and UDP.
- External: will be used with the load balancing function for access outside the cluster. Before using external service, you need to create load balancing cluster and nodes in load balancing first. When creating external service, a load balancing instance will be created in load balancing synchronously.
- Load balancing network: select IP subnet, the system will automatically assign an IP address from the IP subnet as the access IP.
- Target port: The target port is the port on the pod.
- Service port: The external user access port.
- Protocol: Select the protocol used by the application, including TCP and UDP.
- Internal: A ClusterIP will be automatically generated for access inside the cluster and between container groups.
- Restart Policy: Only supports always, which means the container always restarts the container when it exits.
- Advanced configuration: Configure tags and notes according to requirements.
- Tag: Customize to set the tag of statefulset application.
- Remarks: Customize setting remarks information for statefulset applications.
- Containers: You can set one or more different containers for a pod in deployment according to the requirements.
-
Name: Customize the container name.
-
Container image: If you only enter the image name, the default is to use the image on dockerhub, if you need to use the private repository image, you need to set the repository/image. This example directly enter nginx.
-
CPU/Memory: set the CPU and memory size occupied by the container.
-
Container commands, command parameters: set the container commands and parameters. The container naming corresponds to spec.containers.command, and the parameters correspond to spec.containers.args. e.g. command: [“perl”, “-Mbignum=bpi”, “-wle”, “print bpi(2000)"] in the yaml file, you need to enter the following information in form container command to enter the following information.
$ perl -Mbignum=bpi -wle print bpi(2000) -
Data volume: Set the storage declaration and mount point for the container in Pod by key-value pair, you need to create the storage volume declaration in the namespace under the cluster in advance.
-
Environment variables: Configure environment variables for Pods in the form of key-value pairs. Used to add environment flags to Pods or pass configuration, etc.
-
Privileged mode: Privileged mode has the same privileges for processes inside the container as for processes outside the container.
-
-
Click the “Deploy” button to deploy the nginx application.
Set Image
This function is used to modify the container image of a statefulset application.
- On the statefulset page, click the “Set Image” button on the right action bar of the statefulset application to bring up the Set Image dialog box.
- Set the image and click the “OK” button to modify the container image of the application.
Set the number of copies
This function is used to modify the number of container copies of the statefulset application.
- On the Statefulset page, click the “Set Copy Number” button on the right action bar of the statefulset application to bring up the Set Copy Number dialog box.
- Set the number of copies and click the “OK” button to set the number of container group copies.
View/Edit
This function is used to view or edit the yaml file of the statefulset application.
- On the statefulset page, click the “More” button on the right action bar of the statefulset application, and select the drop-down menu “View/Edit” menu item to bring up the View/Update dialog box.
- Support to view and edit the information of yaml file with status application.
- After editing the yaml file, click “OK” button to take effect.
Delete Statefulset Application
This function is used to delete statefulset applications, and container groups (pods) created by statefulset applications.
Individual Deletion
- On the statefulset page, click the “More” button on the right action bar of the statefulset application, select the drop-down menu “Delete” menu item, and the action confirmation dialog box pops up.
- Click the “OK” button to delete the statefulset application and related resources.
Batch Delete
- Select one or more statefulset applications in the statefulset list, and click the “Delete” button at the top of the list to bring up the action confirmation dialog.
- Click the “OK” button to delete the statefulset apps and related resources.
View Statefulset Application Details
This function is used to view the statefulset application details.
- On the Status page, click the Status Application Name item to enter the Status Application Details page.
- View the following information: Cloud ID, ID, name, status, cluster, namespace, container group, image, initialized image, tag, created at, etc.
View Container Group
This function is used to view the container groups created by statefulset applications and supports managing container groups.
View/Edit
This function is used to view the yaml file of a container group.
- On the statefulset page, click the statefulset application name item to enter the statefulset application details page.
- Click the Container Groups tab to enter the Container Groups page.
- Click the “View/Edit” button on the right column of the container group to bring up the View/Update dialog box.
- Support viewing and editing yaml file information of statefulset applications.
- After editing the yaml file, click the “OK” button to take effect.
Delete
This function is used to delete a container group. After the container group is deleted, a new container group will be redeployed according to the yaml file settings.
- On the Statefulset page, click the Statefulset Application Name item to enter the Statefulset Application Details page. Click the Container Groups tab to enter the Container Groups page.
- Click the “Delete” button on the right action bar of the container group to bring up the action confirmation dialog box.
- Click the “OK” button to complete the operation.
View Service
This function is used to view the services created by statefulset applications. You can view the corresponding services only if the internal or external services are set at the time of creation.
View/Edit
This function is used to view the service’s yaml file.
- On the Statefulset page, click the Statefulset Application Name item to enter the Statefulset Application Details page.
- Click the Services tab to enter the Services page.
- Click the “View/Edit” button on the right side of the service to bring up the View/Update dialog box.
- You can view and edit the yaml file information of the statefulset application.
- After editing the yaml file, click the “OK” button to take effect.
Delete
This function is used to delete a service.
- On the Status page, click the Status application name item to enter the Status application details page.
- Click the Services tab to enter the Services page.
- Click the “Delete” button on the right column of the service to bring up the action confirmation dialog box.
- Click the “OK” button to complete the operation.
View Events
This function is used to record the occurrence of resource object events, including the content, source, cause, and created at, for troubleshooting purposes.
- On the Statefulset page, click the Statefulset Application Name item to enter the Statefulset Application Details page.
- Click the Events tab to enter the Events page. View the content, source, reason, and created at of the event.
View source information
This function is used to view and edit the yaml information of the statefulset application.
- On the Statefulset page, click the Statefulset Application Name item to enter the Statefulset Application Details page. Click the “Source Information” tab to enter the source information page.
- Click the “Copy Content” button to copy the yaml file information of the node.
- After updating the yaml file, click the “Update” button.
View Operation Log
This function is used to view the operation logs related to statefulset applications.
- On the statefulset page, click the statefulset application name item to enter the statefulset application details page.
- Click the Operation Log tab to enter the Operation Log page.
- Load More Logs: In the Operation Logs page, the list shows 20 operation logs by default. To view more operation logs, please click the “Load More” button to get more logs.
- View Log Details: Click the “View” button on the right column of the operation log to view the log details. Copy details are supported.
- View logs of specified time period: If you want to view the operation logs of a certain time period, set the specific date in the start date and end date at the top right of the list to query the log information of the specified time period.
- Export logs: Currently, only the logs displayed on this page are supported to be exported. Click the upper-right corner of
 icon, set the export data column in the pop-up export data dialog, and click the “OK” button to export the logs.
icon, set the export data column in the pop-up export data dialog, and click the “OK” button to export the logs.